Scientists are still learning about how cannabis works in our brains and bodies. For hundreds of years, we knew that cannabis got us high, but not how it made us feel that way. Luckily, research eventually revealed the existence of the endocannabinoid system.
So what is the endocannabinoid system? Honestly, learning about it can be confusing and technical. We’re here to break down the endocannabinoid system in a simple way so you know a little more about how cannabis functions in your body.
What Is the Endocannabinoid System?
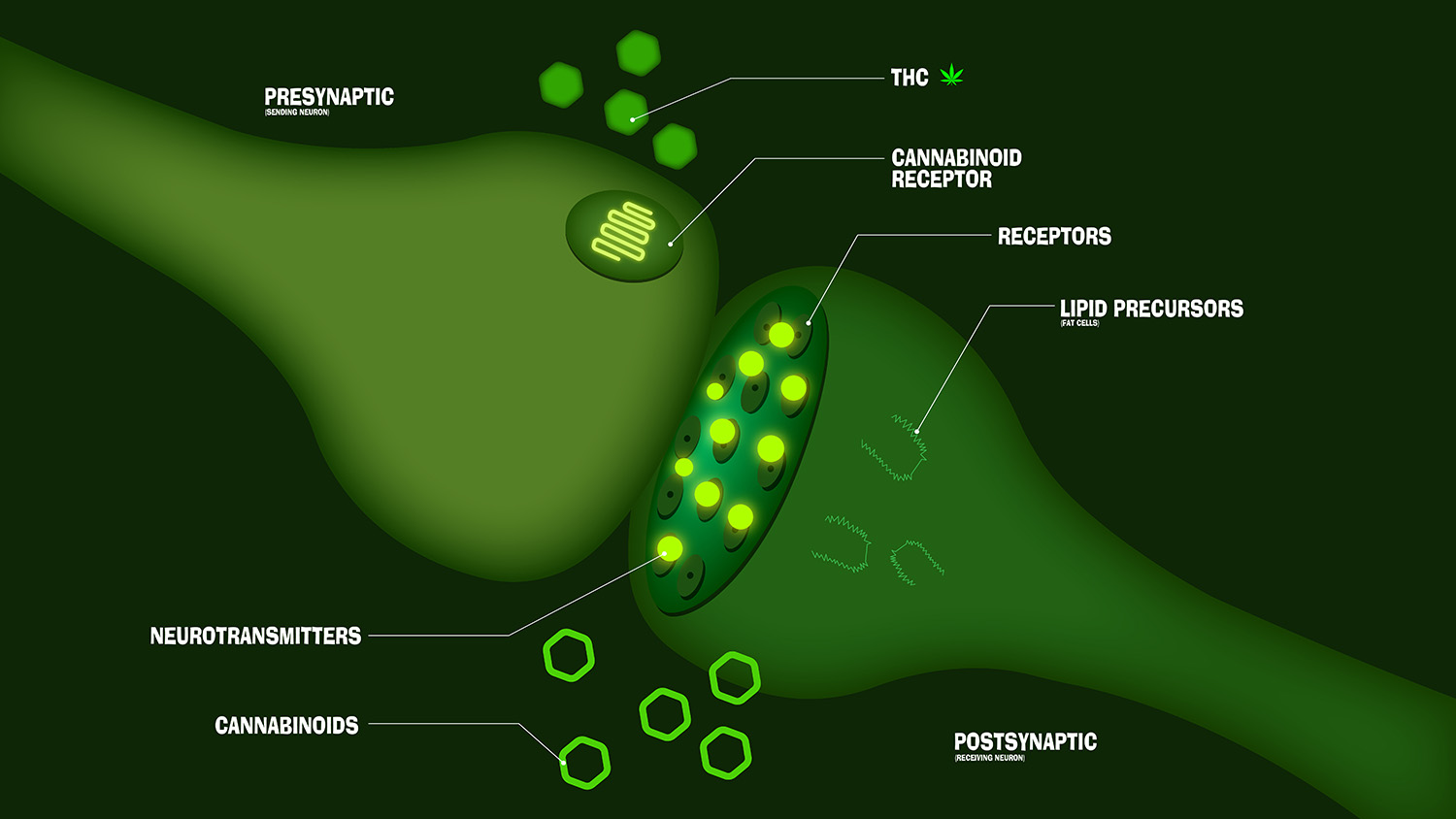
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a large network of receptors found throughout our bodies. It was discovered in the 1990s during research about THC. The ECS handles the regulation of endocannabinoids and cannabinoids in your body.
Cannabinoids are the chemicals found in the cannabis plant like THC and CBD. Endocannabinoids are chemically similar to cannabinoids, but they are made by your body. The two main endocannabinoids scientists have discovered are:
- Anandamide (AEA)
- 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
Your body has two cannabinoid receptors: CB1 and CB2. Think of the receptors as locks and endocannabinoids as keys. The keys are able to open the locks and gain entries into your cells.
CB1 receptors are found in your central nervous system and brain, and they are one of the most numerous types of receptors there. They control the levels of most of your brain’s neurotransmitters and regulate them by acting on immediate feedback.
Your CB2 receptors exist mostly in your immune tissues. They aren’t stimulated by cannabis in the same way as the CB1 receptors are, so they won’t get you high, which can be an unwanted side effect for many medical patients.
Experts are still trying to figure out the nuances of the ECS and exactly how it works. However, we do know that it’s responsible for many different functions in your brian and body.
What Are the Functions of the Endocannabinoid System?
The ECS handles a wide variety of functions in your body. The main one is to achieve homeostasis, or an internal environment that remains consistent even as the outside world changes. Your ECS keeps your various bodily systems in balance.
Endocannabinoid receptors are found throughout your body, including in your brain, organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells. The ECS regulates these body systems through immediate feedback, turning certain activities up or down when a system needs to be adjusted.
Some of the processes the ECS regulates include:
- Appetite and digestion
- Metabolism
- Chronic pain
- Stress
- Mood
- Sleep
- Learning and memory
- Motor control
- Skin and nerve function
- Inflammation and other immune system responses
- Cardiovascular system function
- Muscle formation
- Bone remodeling and growth
- Liver function
- Reproductive system function
As you can see, these systems have huge impacts on the way your body works. So what happens when you add cannabis to the mix?
How THC & CBD Affect the Endocannabinoid System
There are over 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant, but the two most popular are THC and CBD. They bind to the same receptors as the natural endocannabinoids do, and they have a strong impact on your brain and body when you consume cannabis.
THC
THC is the compound in cannabis that gets you high. Whether you smoke weed, vape, dab, or eat an edible, THC enters your body and interacts with your ECS.
THC binds to your body’s CB1 and CB2 receptors in the same way that natural endocannabinoids do. It has a particularly strong effect on your CB1 receptors, which produce the psychoactive effects of THC.
THC can cause many changes to your brain and body, including:
- Changes in mood (euphoria)
- Changes in consciousness
- Relaxation
- Memory processing
- Motor control
- Energy levels
The amazing benefits of THC are created by your body’s ECS. Some of the common medical conditions that can be treated with THC include:
- Chronic pain
- Sleep issues
- Depression and anxiety
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Nausea, specifically for cancer patients
- Epilepsy
- HIV/AIDS
- Multiple sclerosis
- Glaucoma
- Opioid dependence
- Fibromyalgia
- Arthritis
- Anorexia
- Tremors
CBD
CBD is a nonpsychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Experts still aren’t entirely sure how CBD interacts with your body’s endocannabinoid system, but it doesn’t bind to either the CB1 or CB2 receptors.
One theory is that it prevents cannabinoids from being broken down in your body, which makes them affect you more strongly. It may also bind to a cannabinoid receptor that we haven’t discovered yet.
By itself, CBD may interact with the endocannabinoid system to help patients with:
- Depression
- Cancer
- Chronic pain
- Epilepsy
- Parkinson’s disease
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Inflammation
- Migraines
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Psychosis
- Stress
- Acne
- Anxiety
- Addiction
- Schizophrenia
- Insomnia
So now you can answer the question, “What is the endocannabinoid system?” But what does it mean for you as a cannabis consumer?
For one thing, it’s cool to know how your body processes cannabis. Before the ECS was discovered, we weren’t sure why THC made us high. Scientists now have the framework to continue to study the effects of cannabis and its medical benefits.
For another, you now know the profound impact cannabis can have on your brain and body. Whether you’re looking for the euphoric effects of THC or the pain-relieving properties of CBD, you have your endocannabinoid system to thank for the ride.
Ready to stimulate your ECS? Blackstone Valley Cannabis can help!
We sell only the freshest cannabis in Uxbridge, MA, and we’re passionate about serving our local community. We carry a wide range of cannabis products, including:
Visit our dispensary to talk to our expert dispensary agents, or place an order online for easy pickup today!